You are here :
- CY Transfer
- Home
- Develop
- Collaboration tools
Collaboration tools
HOW?
What types of partnership with the university can a company enter into?
There are different types of agreement depending on the nature of the partnership. They each have their specific features in terms of duration and management of Intellectual Property (IP). All this is summarised in the table below:
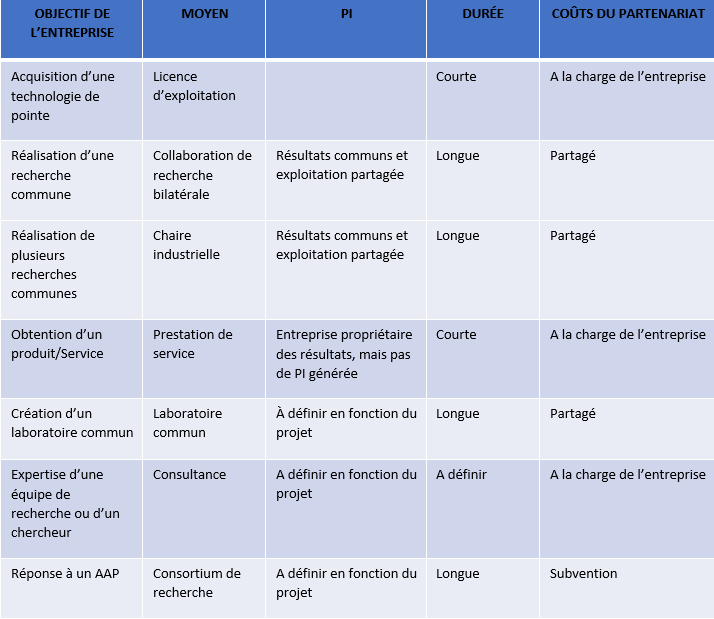
There is an additional tool possible: sponsorship. For further information, please contact CY Fondation.
WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES?
What advantages can a company draw from working with a university?
Le Crédit d'Impôt Recherche (CIR) (Research Tax Credit)
The CIR is a tax scheme which allows companies to reduce their tax payments based on their R&D expenditure during the calendar year. The CIR is therefore a fiscal lever aimed at fostering research and development (R&D) efforts undertaken by companies, irrespective of their size or industry. This scheme is governed by Article 244 Quater 4 of the Code général des impôts (CGI) (General Tax Code), which sets all the parameters and criteria that every company has to follow for each CIR declaration. There is a 30% tax deduction on the expenditure covered by the partnership agreement in basic research, applied research, and experimental development.
For more information: CIR
Le Crédit d'Impôt Innovation (CII) (Innovation Tax Credit)
The CII is a tax measure reserved for SMEs. The latter can benefit from a 20% tax credit on the expenditure required for designing prototypes or pilot plants for new products. The eligible amount is capped at €400,000 per year per company. The declaration is made using the same form Cerfa N° 2069-A-SD and in the same way as with the Research Tax Credit (CIR). In certain circumstances, an SME can receive their CII payment in advance.
For more information: CII
Le Crédit d'Impôt Collaboration de recherche (CICO) (Research Collaboration Tax Credit)
Article 69 of the 2022 Loi de Finances (Finance Act) created the Research Collaboration Tax Credit (CICO) in order to encourage companies to conduct R&D work in partnership with research and knowledge dissemination organisations.
Its primary goal is to create an incentive for companies (especially SMEs and start-ups) to engage in R&D activities as part of joint research.
Its definition is in line with European rules on state aid:
- A separate scheme from CIR;
- Restrictions on the R&D costs borne by the companies and incurred by the research and knowledge dissemination organisations as part of an effective research partnership;
- Compliance with the aid intensities authorised by the General Block Exemption Regulation (GBER) on research, development, and innovation (RDI) aid.
The tax credit is equivalent to 50% of the eligible costs deducted (for a maximum of 6 million euros of declared costs) in the case of SMEs. It is 40% in the case of intermediate-sized enterprises (entreprises de taille intermédiaire (ETI)) and large enterprises (grandes entreprises (GE)), for a maximum of 6 million euros of declared costs.
The rates are the same for all the various categories of R&D projects (basic research, applied research, and experimental development).
These rates exhaust the maximum aid intensities authorised for RDI state aid in the absence of any distinction between the various categories of R&D projects.


